
Lab with Artificial Intelligence
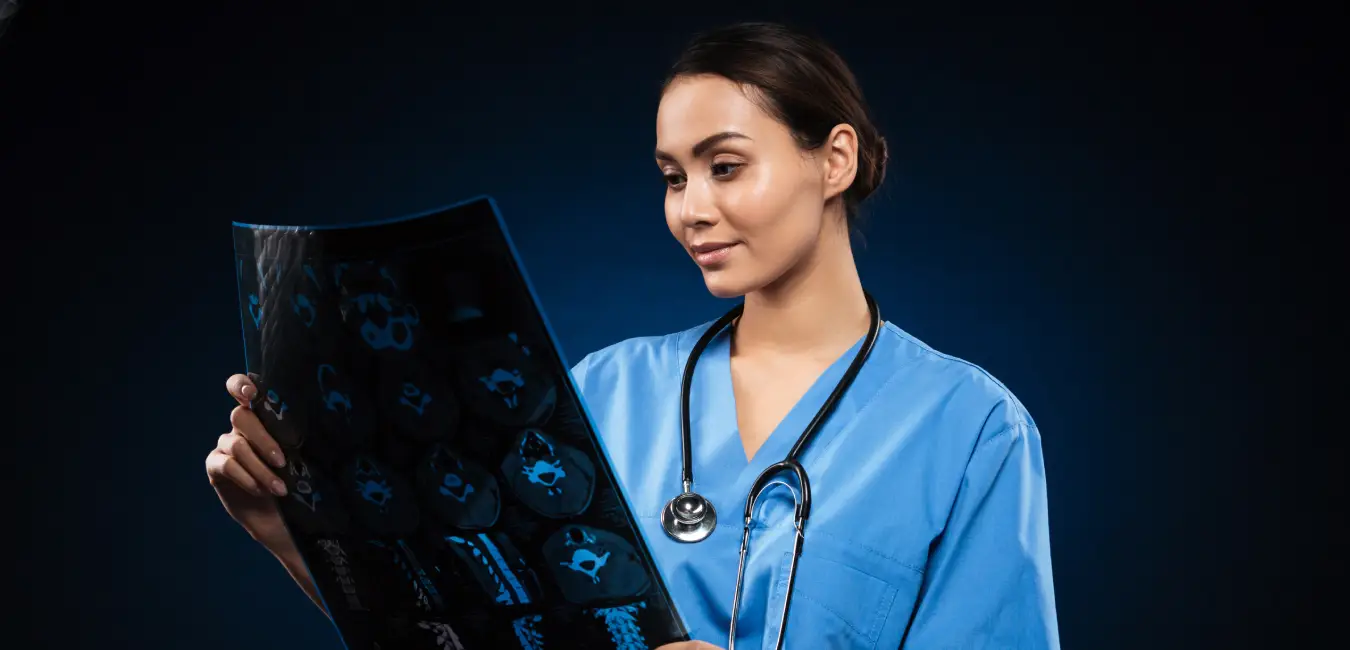

X-Rays are a type of imaging test that uses electromagnetic radiation to create pictures of the inside of the body. They help doctors examine bones, chest, teeth, and internal organs to detect fractures, infections, tumors, or abnormalities. X-rays are quick, painless, and one of the most common diagnostic tools in medicine.
X-rays are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation that can pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bone.
When X-rays pass through the body, they produce images on a detector or film — showing different shades of black, white, and gray depending on tissue density.
X-Rays are a type of imaging test that uses electromagnetic radiation to create pictures of the inside of the body. They help doctors examine bones, chest, teeth, and internal organs to detect fractures, infections, tumors, or abnormalities. X-rays are quick, painless, and one of the most common diagnostic tools in medicine.
Purpose: To examine the lungs, heart, and chest wall. Common Uses: Detect pneumonia, tuberculosis, or lung cancer Evaluate heart enlargement (cardiomegaly) Identify fluid accumulation (pleural effusion) View Types: PA (Posteroanterior) View – standard chest view Lateral View – side view for depth and clarity
Purpose: To view digestive organs and detect problems in the abdomen. Common Uses: Intestinal obstruction Kidney or gallstones Swallowed foreign objects Free air (perforation) in the abdomen
Purpose: To visualize bones and joints. Common Uses: Fractures and dislocations Arthritis or bone infection (osteomyelitis) Bone tumors or osteoporosis
Purpose: Used by dentists to examine teeth and jaw structures. Types: Bitewing: Detects cavities between teeth. Periapical: Shows the entire tooth root and surrounding bone. Panoramic: Displays all teeth and jaws in one image.
Private X-Ray scans are provided on a per fee basis and are not covered by health care.