
Lab with Artificial Intelligence
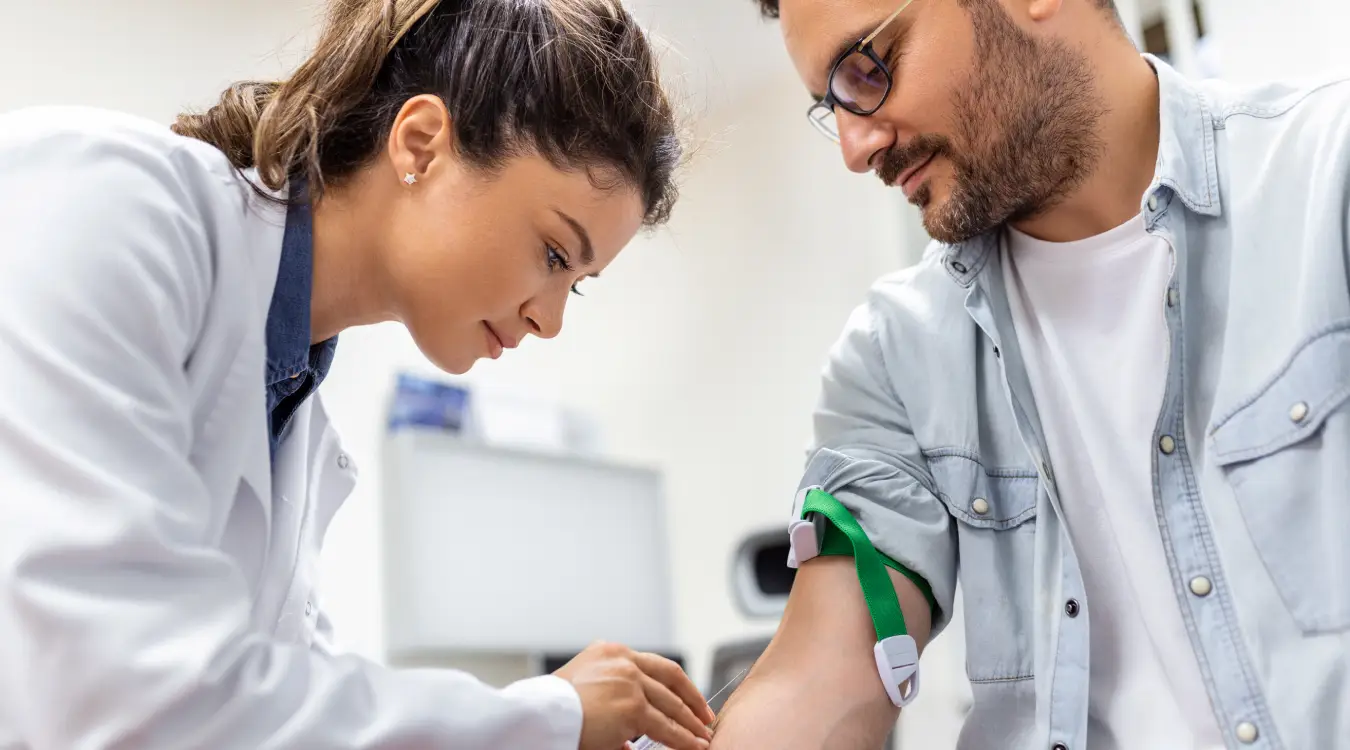

A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is one of the most common blood tests used in healthcare. It provides important information about the cells in your blood — red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. The test helps doctors evaluate your overall health and detect a wide range of disorders, including anemia, infection, and blood cancers.
Limpid General is constantly thinking and going beyond for our patients, our community and our people. As people and communities change, Limpid General will continuously evolve to meet their needs. We are driven to achieve the promise of people-centered care - to create a welcome and inclusive environment that contributes to health equity.
RBCs carry oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and return carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
WBCs are part of the immune system and help fight infection. WBC Count: Total number of white blood cells. Differential Count: Measures different types of white blood cells: Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes Eosinophils Basophils
Increased WBCs (Leukocytosis): May suggest infection, inflammation, stress, or leukemia. Decreased WBCs (Leukopenia): May indicate bone marrow suppression, autoimmune disease, or viral infection.
Platelets help the blood clot and stop bleeding. Platelet Count: Number of platelets in the blood. Mean Platelet Volume (MPV): Average size of platelets.
Low Platelet Count (Thrombocytopenia): May cause easy bruising or bleeding; can be due to bone marrow disorders, infections, or autoimmune diseases. High Platelet Count (Thrombocytosis): Can increase risk of clotting or signal inflammatory or bone marrow conditions.
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a routine yet vital laboratory test that evaluates the cellular components of blood